Reducing CO2 emissions to address climate change,
Promoting the use of renewable energy, etc.
Basic Concept
We regard climate change risk as one of the greatest risks facing our Group, and will promote modal shifts by introducing energy-efficient vehicles (trains and buses) and using renewable energy, while also expanding the acquisition and development of green buildings.
CO2 reduction and energy/resource conservation activities
Towards "carbon neutrality by 2050"
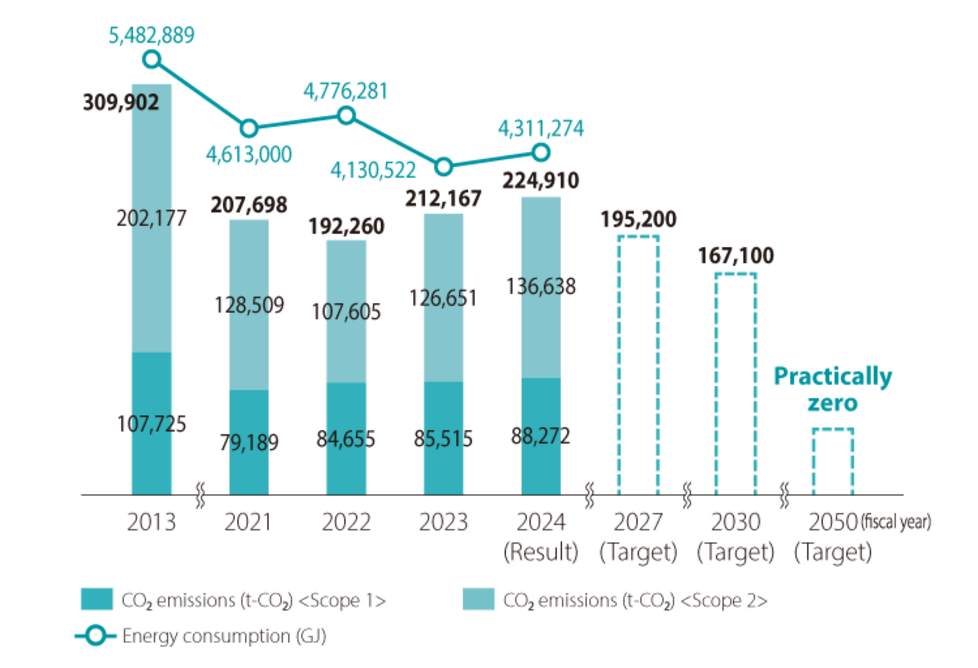
The Group has set a goal of reducing CO2 emissions by more than 46% by fiscal 2030 compared to fiscal 2013 levels.
Emissions in fiscal 2024 will be 224,910 tons, a 27.4% reduction from the base year of 2013, which was 309,902 tons.
We will continue to introduce energy-saving vehicles and promote the introduction of highly energy-efficient equipment in our real estate and distribution facilities, with the aim of achieving the goals of the Nankai Group Environmental Vision 2030. The Group has set a target of virtually zero CO2 emissions by 2050, and will consider and implement all possible measures, including energy-saving measures as well as the introduction and utilization of renewable energy, energy creation, and alternative energy, and the use of carbon offsets.
Supporting the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
The world is facing a climate crisis, with rising average temperatures, extreme heat, and increasing frequency of heavy rain and flooding. Therefore, we have begun efforts to strengthen risk management in anticipation of the impact of climate change on our business and to integrate these measures into our business strategy. In September 2021, we endorsed the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)*, which aims to reduce the risk of financial market instability caused by climate change.
Established in 2015 by the international organization, the Financial Stability Board, the initiative recommends that companies assess their own business risks and opportunities arising from climate change, understand the financial impact, and disclose that information.

Environmental impact data certified by a third party
To increase the reliability of our environmental impact data, our Group has been obtaining third-party assurance for our energy-related CO2 emissions (Scope 1 and 2) since fiscal 2021. In fiscal 2023, we also obtained third-party assurance for the "Nankai Group Energy-related CO2 Emissions Calculation Report (FY2023)" from Deloitte Tohmatsu Sustainability Co., Ltd.
"Independent Third-Party Assurance Report"
March 3, 2025 Third-Party Assurance Report (PDF: 1,318KB)
April 30, 2024 Third-Party Assurance Report (PDF: 2,756KB)
April 28, 2023 Third-Party Assurance Report (PDF: 2,285KB)
Identifying CO2 emissions throughout the supply chain (Scope 3, FY2024)
In addition to CO2 emissions from our group's business activities (Scope 1 and 2), we have been calculating indirect emissions (Scope 3) generated in our supply chain since fiscal 2021. Over the past three years, purchased products and services account for approximately 60% of these emissions.
(Unit: t-CO2)
| Upstream (Procurement) | 1. Purchased products and services | 500,265 | Downstream (sales) | 9. Transportation and distribution (downstream) | – |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2. Capital goods | 123,745 | 10. Processing of sold products | – | ||
| 3. Not included in Scope 1 or 2 Fuel and Energy Related Activities | 37,598 | 11. Use of sold products | 18,811 | ||
| 4. Transportation and distribution (upstream) | – | 12. Disposal of sold products | – | ||
| 5. Waste generated from business operations | 6,142 | 13. Leased assets (downstream) | 114,103 | ||
| 6. Business trips | 1,202 | 14. Franchise | – | ||
| 7. Employee Commuting | 2,195 | 15. Investment | – | ||
| 8. Leased assets (upstream) | – | total | 804,061 | ||
* Supply chain: A series of steps involved in business activities, including procurement, manufacturing, logistics, sales, and disposal of products.
*Categories 4, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, and 15 have been excluded due to their importance.
*Not guaranteed by a third party
Energy-saving measures for railway facilities and vehicles
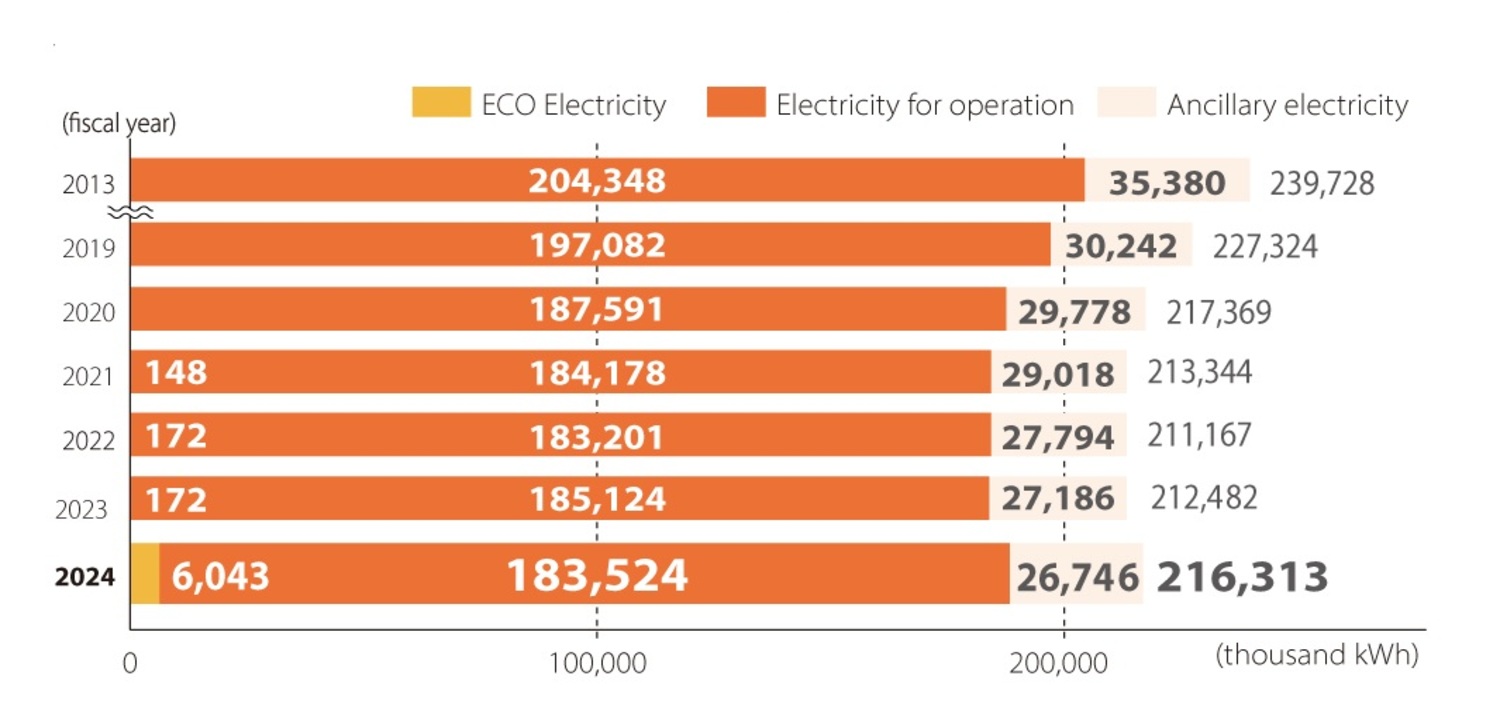
Our railway power consumption in fiscal 2024 will be 216,313,000 kWh (an increase of 1.8% compared to fiscal 2023), of which 188,978,000 kWh will be for train operation, accounting for 87.4% of the total, and the remaining 27,335,000 kWh will be for incidental power. Overall railway power consumption in fiscal 2024 will be reduced by 9.8% compared to fiscal 2013. Incidental power refers to the power used for signaling equipment, level crossing equipment, and station facilities (lighting, air conditioning, elevators, etc.). We are promoting energy-saving initiatives, such as saving electricity in summer and winter (strictly maintaining indoor temperatures, etc.) and gradually switching station lighting to LED.
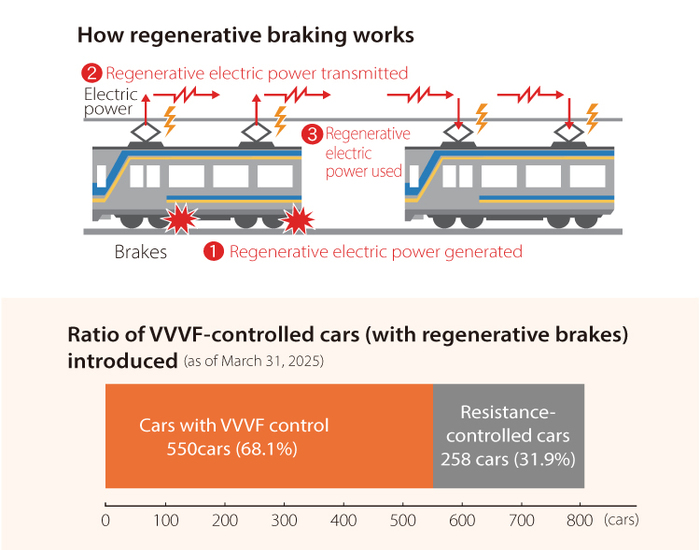
Regenerative braking and VVVF control
"VVVF control" controls AC motors by changing the voltage and frequency, thereby controlling the acceleration and speed of trains.
Unlike conventional vehicles, it does not use electrical resistance, allowing for highly energy-efficient control.
In addition, "regenerative braking" is a system in which the motor acts as a generator when the train brakes, and the generated electricity is returned to the overhead lines to supply other trains traveling nearby. Reusing the generated electricity can reduce the amount of electricity used.
These methods enable a reduction in electricity consumption compared to conventional vehicles, so we are promoting the introduction of vehicles equipped with both functions.
Adoption of a simultaneous feeding system for both up and down lines and installation of power factor improvement capacitors
By connecting the feeder wires (lines that supply electricity to trains) on the up and down lines, we are reducing the resistance to the feeder wires and reducing the power loss consumed by the wires. This allows the regenerative current generated by regenerative braking to flow through the connection, allowing the up and down trains to use it efficiently and reduce power consumption. Furthermore, by installing a power factor improvement capacitor, we are reducing the loss that occurs when electricity is used and improving power efficiency.
Changes in railway power consumption


Energy-saving measures in real estate and distribution facilities
We have updated our existing facilities to more energy-efficient equipment between fiscal 2022 and fiscal 2024. Specifically, we updated the heat source equipment that powers the entire Nankai Terminal Building to more efficient equipment, and also reduced lifecycle costs by changing to an appropriate capacity and number of units according to the current load capacity.
Additionally, by installing inverters that enable load-dependent operation control on the pumps that supply chilled water to every corner of the large-scale facility, we have been able to curb the power required for transportation and reduce electricity usage. Along with updating these facilities, we plan to automate equipment control and optimize and visualize operations by introducing heat source controllers and BEMS (Building Energy Management Systems), further reducing energy usage, along with that of existing facilities.
Operating environmentally friendly buses
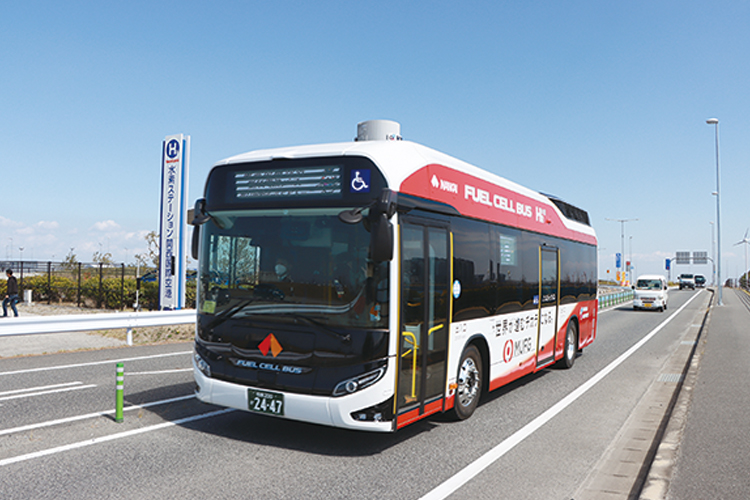
In the bus business, three fuel cell buses that use hydrogen as an alternative energy source to diesel were introduced in fiscal 2021 (two for Tokushima Bus and one Nankai Bus), and electric buses will be introduced sequentially from fiscal 2022 onwards (a total of eight buses will be introduced in fiscal 2024, including six Nankai Bus and two for Nankai Wing Bus), and these have begun operation.
We will continue Contribute to preserving the global environment by reducing environmental impact and realizing a sustainable society.


Utilization of renewable energy
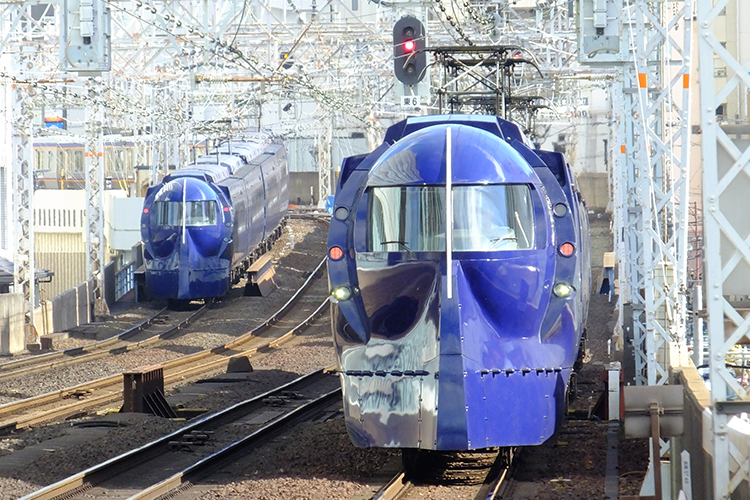
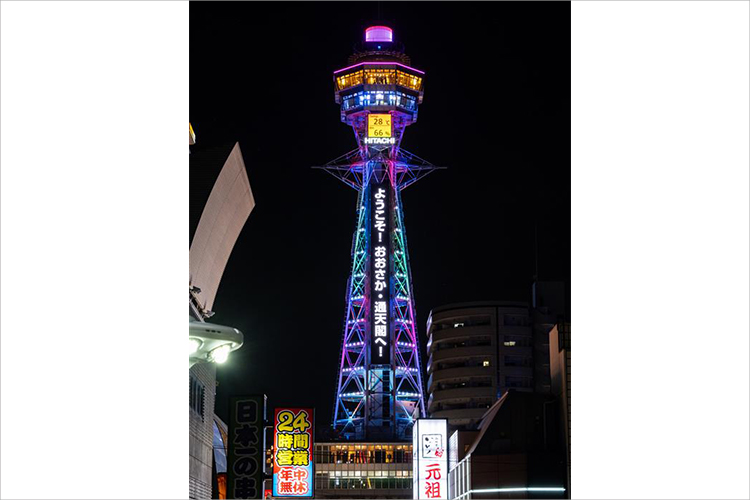
As part of our efforts to reduce CO2 emissions, we will operate all six Kosaku Line (Koyasan cable cars) in June 2021 and limited express Rapi:t in April 2024, and from April 2025, we will switch to 100% renewable energy for the electricity used in Tsutenkaku Tower. In April 2026, the new sightseeing train GRAN Tenku and Limited Express Koya will also run on 100% renewable energy for their runs.
In addition, Namba Parks and NAMBA SkyO have achieved carbon-free electricity for all electricity used at both facilities, including utilizing electricity self-consigned from our Nankai Ominedai solar power plants (approximately 6 million kWh of annual power generation) from our own solar power plants.
In addition, the home shed (Hagoromo Station, Izumiotsu Station, Izumisano Station), the Boat Race Suminoe owned by Suminoe Kogyo Co., Ltd. (Osaka-shi Suminoe Ward), the Tannowa Solar Power Plant (Sennan-gun Misaki-cho, Osaka Prefecture) and Osaka Prefectural Food Products Distribution Center Solar power generation facilities are installed in Building E (Ibaraki City, Osaka Prefecture). The Group will continue to consider and implement the use of new renewable energy.




Contribution to modal shift
The CO2 emissions per unit of transport volume of railways and ships (ferries) operated by our group are approximately 1/7 * of that of private passenger cars for railways and approximately 1/5 * of that of commercial freight vehicles for ships, and are considered to be one of the effective means of reducing CO2 emissions in passenger and freight transport.
Our group has formed a public transportation network centered on railways, and is promoting urban development centered around stations, contributing to the development of local communities and the creation of a carbon-neutral society.
Source: Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism "Carbon dioxide emissions per transport volume (passengers) 2023"
Register as a ZEH developer
We have registered as a ZEH developer as defined by the Environmental Co-Creation Initiative, a general incorporated association.
A ZEH (Net Zero Energy House) is a house that aims to achieve a net zero annual primary energy consumption balance by significantly improving the insulation performance of the exterior shell, introducing highly efficient equipment systems to achieve significant energy savings while maintaining the quality of the indoor environment, and by introducing renewable energy sources.
ZEH developers are building owners (apartment developers, owners, etc.) and construction companies (general contractors, house manufacturers, and other construction companies) who play a central role in forming ZEH-M projects by publicly disclosing their "plans for promoting ZEH-M," "progress," "ZEH-M implementation plans," and "ZEH-M implementation results" based on the purpose of the ZEH (Net Zero Energy House) demonstration project.

ZEH-M implementation record
| Apartment name | location | Completion date | ZEH-M rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Southern Crest Namba Minami | Osaka City | October 2023 | ZEH-M Oriented |
Information disclosure through responses to CDP
CDP (Carbon Disclosure Project) is a project in which institutional investors work together to ask companies to disclose their climate change strategies and specific greenhouse gas emissions. We respond to CDP questionnaires on climate change and water every year.
| Our CDP Score | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | FY2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate change | B | B | B | A- | B |
| Water | B | B | B | C | B |





